Federal Income Tax Brackets for Freelancers and Gig Workers
As a freelance or gig worker, you may face unique tax challenges. Many independent workers may not see a steady paycheck each month. Your income can swing widely in a short time span. That level of unpredictability may make it hard to plan your taxes. In this blog, we will dig into federal income tax brackets and how they affect your earnings. You may gain insight into which tax tier might apply to your net income. We can help you build a plan to set aside cash. By knowing how much you may owe, you can reduce your stress. You may also learn to forecast and adjust as your income shifts.
Why Understanding Tax Brackets Matters
Avoiding Large Tax Bills
Many freelancers do not have tax withheld from earnings. This may leave a large tax bill at year-end. Without a plan, you may not know what to save.
Projecting and Reserving the Right Cash
Knowing your place in the Federal Income Tax brackets helps you plan and save cash well. This knowledge can lower the risk of paying too much tax. A clear plan also helps keep your cash flow steady.
Building a Buffer for Smooth Payments
You may build a buffer to pay taxes on time. Planning ahead gives you more control over your finances. It can help avoid stress when tax season arrives.
How Tax Tiers Apply to Freelancers and Gig Workers
Determining Taxable Income for Freelancers
Freelancers pay tax on the income they earn each year. You can subtract business costs from your total income easily. This net income is the base for your yearly tax.
How Income Affects Tax Tiers
Net income may shift within federal income tax brackets each year. If income grows, you may move to a higher tier. This change may raise the total tax you need to pay.
Impact of Business Costs on Tax Brackets
If costs rise, you may drop into a lower tax tier. This is key for short-term or seasonal freelance work. Work hours or clients may change your total net income.
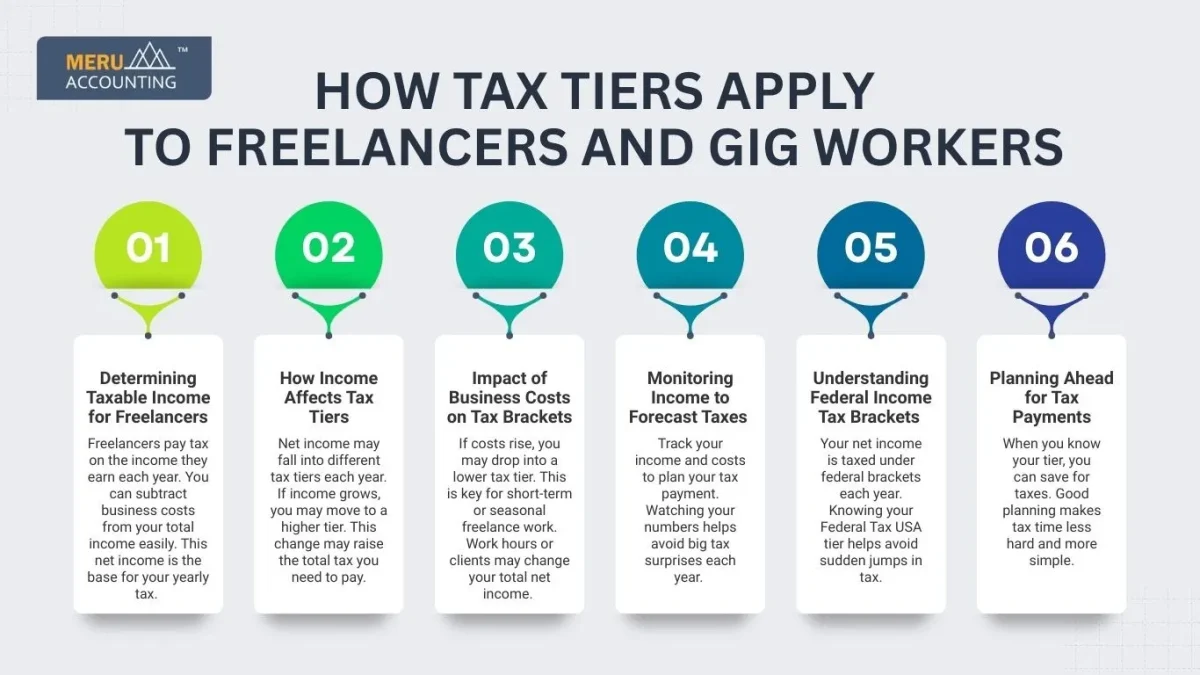
Monitoring Income to Forecast Taxes
Track your income and costs to plan your tax payment. Watching your numbers helps avoid big tax surprises each year.
Understanding Federal Income Tax Brackets
Your net income is taxed based on federal income tax brackets set each year. Knowing your tax tier helps avoid sudden jumps in tax.
Planning Ahead for Tax Payments
When you know your tier, you can save for taxes. Good planning makes tax time less hard and simpler
2025 Tax Rate Tiers for Freelance Income
To plan well, you may need to know the projected federal income tax brackets for 2025. In some scenarios, one tier may be low, like ten percent on lower earnings. Higher tiers may rise to twenty-two percent or more as income grows. Those projected ranges may shape your yearly set‑aside plan. Because your profits may fluctuate, you may hit different tax tiers during the year. That uncertainty may push you to save more than you think. If you under‑reserve, you may owe a larger bill at year’s end. Conversely, if you over‑reserve, you may have cash you cannot use. You may want to revisit your plan mid‑year to adjust for real income shifts.
For instance, if your net income climbs above a given threshold, you may end up in a higher tier. That may raise your marginal tax rate and your tax burden. You may also want to use tools or a tax pro to model different income paths.
Tax Planning Tips for Freelancers
Here are some strategies you may use to manage your tax burden:
- Estimate your income and costs monthly or quarterly to forecast liability.
- Set aside a fixed percentage of each payment into a tax savings fund.
- Use a spreadsheet or app to track your income, expenses, and cash flow.
- Pay estimated taxes every quarter to spread your burden.
- Build a cash reserve specifically for taxes to buffer shocks.
- Adjust your estimated tax payments if your income changes sharply.
- Use retirement accounts to reduce your taxable net income.
- Keep solid records to maximize your deductions and lower your base.
- Revisit your plan mid-year to account for surprises or growth.
- Consult a tax professional if your earnings or costs become complex.
By doing that, you may better align your savings with your projected tax bill. You may avoid paying too little or locking too much cash away.
Challenges Faced by Gig Workers
Income Variability
Many gig workers do not get a set monthly pay. Earnings can change a lot if the client’s work shifts. Income swings may move workers into higher tax rates.
Tax Planning Difficulties
Without planning, workers may pay too much tax. Saving too much may limit money for bills. Not tracking costs can raise taxable income.
Payment Responsibilities
Missing quarterly taxes may cause IRS fines. No employer withholding means full tax responsibility. Balancing tax savings with bills can be tough.
Access to Advice and Bookkeeping
Many gig workers lack tax help or guidance. Wrongly applying costs may lead to tax errors. Poor bookkeeping can make net income unclear.
Estimated Tax Payments and Your Federal Income Tax Brackets
Understanding Estimated Taxes
Freelancers often pay taxes four times a year. Payments are based on your expected income and your spot in the federal income tax brackets.
Calculating Payments
Split the yearly income into four parts to pay. Use IRS Form 1040-ES to check amounts.
Change payments midyear if income shifts.
Importance of Accuracy
Paying too little may bring fines or interest. Paying too much keeps money tied up with the government. Good estimates help match payments to actual tax.
Saving for Retirement While Managing Taxes
1. Traditional IRA Contributions
- Giving to a traditional IRA can cut your taxable income.
- Lower income may help you stay in a smaller tax bracket.
2. Fixed Percentage Savings
- Save a fixed share of your freelance income each month.
- Regular saving over time slowly grows your retirement funds.
3. Small Business Retirement Plans
- SEP IRA or Solo 401(k) lets you save more yearly.
- Taxes are paid later, when you withdraw the money.
4. Tax-Deferred Growth
- Retirement accounts grow without paying tax at the first stage.
- You pay tax later, which may lower your lifetime tax rate.
5. Adjusting Contributions
- Add more to savings when your income rises each month.
- Cut back in low-earning months to keep cash in hand.
6. Professional Guidance
- Tax pros help pick the best retirement saving plan.
- Planning keeps retirement savings in line with tax needs.
7. Long-Term Goals Alignment
- Retirement savings should match your long-term money goals clearly.
- Check savings often to keep tax benefits high always.
Business Structure and Record Keeping
1. Tracking All Expenses
- Track costs like travel, tools, apps, and meals yearly.
- Careful expense tracking lowers your total taxable income significantly.
2. Using Digital Tools
- Apps or spreadsheets make bookkeeping easy each working day.
- Digital tools give fast, clear reports of all spending.
3. Choosing a Business Structure
- Options include sole prop, LLC, or a small corporation.
- Your structure affects taxes, risk, and allowed deductions.
4. Impact on Self-Employment Tax
- Some structures can cut your self-employment tax amounts.
- Tax pros can check possible savings before filing returns.
5. Organizing Receipts and Records
- Keep all receipts for business spending every single year.
- Organized records make filing taxes simple, smooth, and correct.
6. Year-End Reconciliation
- Match income and costs carefully before you file returns.
- Find missed expenses or deductions you may have overlooked.
7. Professional Consultation
- Tax pros advise on structure and book management.
- Good guidance helps cut taxes and claim all deductions.
State Tax and Its Interaction with Federal Brackets
1. Understanding State Tax Rates
- States may have flat or tiered tax rates.
- Knowing your rate helps plan your full tax payment well.
2. Combined Tax Burden
- Total taxes include federal plus state taxes each year.
- High state rates can raise your overall total tax amount.
3. Planning Cash Flow
- Set aside separate funds for state and federal taxes.
- Planning ahead avoids surprises when quarterly taxes are due.
4. State-Specific Deductions
- Some states give deductions that federal rules do not allow.
- Using them cuts taxable income and total taxes owed easily.
5. Consulting Local Tax Experts
- State rules can be complex and differ a lot.
- Experts help plan state and federal taxes together well.
6. Quarterly State Payments
- Some states require estimated tax payments like the federal rules.
- Pay on time to avoid penalties and extra interest later.
7. Monitoring Law Changes
- State tax rules change often and can affect your plans.
- Staying updated keeps you in line and cuts tax risk.
Estimating Your Tax Liability
1. Calculate Gross Income
- Include all freelance and gig earnings for correct tax estimates.
- Make sure no income is missed while figuring the total tax.
2. Deduct Business Expenses
- Subtract eligible costs to find your net taxable income clearly.
- This lowers your total taxable income and bracket risk.
3. Apply Projected Tax Rates
- Use IRS tables to check taxes owed on net income.
- Helps plan quarterly payments and avoid year-end surprises.
4. Scenario Planning
- Plan for high- and low-income cases to stay ready always.
- Good planning helps manage busy months or slow months smoothly.
5. Track Changes in Income
- Update tax numbers when freelance earnings go up or down.
- Prevents penalties and surprise bills at the end.
6. Monitor Estimated Payments
- Compare estimated payments made versus taxes you expect owing.
- Adjust remaining payments if income or estimates change quickly.
7. Seek Expert Review
- Tax pros review your numbers for correctness before filing.
- Ensures all math is right and avoids costly mistakes later.
Tax Credits That Affect Your Tax Rate
1. Earned Income Credit
- This credit cuts the total tax for eligible low-income workers.
- Lowers your effective tax without changing your tax bracket.
2. Retirement Savings Credit
- Putting money in retirement accounts may give a credit.
- Cuts taxes owed while helping you save for retirement.
3. Health Coverage Credit
- Some health costs can qualify for a tax credit each year.
- The credit lowers overall taxes owed for that year.
4. Business Investment Credits
- Credit may apply to business costs like new equipment bought.
- Encourages reinvestment while lowering total taxes owed effectively.
5. Education and Training Credits
- Approved learning costs can lower your total tax liability.
- Helps gig workers gain skills at a lower cost.
6. Maximizing Credits Strategically
- Track and use all credits during the year carefully, always.
- Applying credits lowers your effective tax rate noticeably each year.
7. Professional Advice
- Tax pros ensure all credits are applied the right way.
- Avoid missing deductions and cut taxes owed efficiently every year.
Working with a Tax Professional
1. Forecasting Tax Scenarios
- Experts model taxes based on changes to your place in the federal income tax brackets.
- Helps plan quarterly payments and avoid surprises later.
2. Retirement Plan Guidance
- Pros suggest plans that cut taxable income effectively each year.
- Align contributions with income changes to gain maximum benefit.
3. Business Structure Optimization
- Tax advisors suggest a structure to lower taxes and increase savings.
- Helps manage self-employment tax and claim allowed deductions.
4. Quarterly Payment Planning
- Ensure estimated payments match projected tax amounts precisely.
- Adjust for income changes to avoid penalties during the year.
5. Credit Maximization
- Professionals find and apply all credits you can use.
- Cuts the effective tax burden noticeably each tax year properly.
6. Record Review and Compliance
- Experts check books and records for accuracy before filing returns.
- Ensures compliance with federal and state tax rules always.
7. Long-Term Tax Strategy
- Pros guide ongoing planning for long-term tax efficiency clearly.
- Cuts surprise taxes and brings peace of mind financially.
Meru Accounting provides accounting and bookkeeping services for freelancers and gig workers. Our team tracks income, expenses, and taxes all year. We track federal income tax brackets and net income to make your tax plan smooth and clear. We maximize deductions and manage taxes efficiently. Partner with us to keep your finances organized and on track.
FAQs
- What are the federal income tax brackets for freelancers?
There is a range of income levels that determine your tax rate. Your net earnings decide which bracket you fall into.
- How do these tax brackets impact gig workers?
They help estimate how much tax you may owe yearly. Higher earnings may place you in a higher bracket.
- Can freelancers move between tax brackets?
Yes, changes in income can shift you into a different bracket. A rise in earnings may increase the amount of tax you pay.
- Do tax brackets affect quarterly estimated tax?
Yes, your expected bracket helps guide quarterly payments. Good planning may help avoid penalties or large bills.
- How is taxable income calculated?
Taxable income is your net earnings after deducting business expenses. This amount determines your tax bracket.
- Does entering a higher bracket increase tax on all income?
No. Only income within that range is taxed at the higher rate. Lower income portions stay taxed at lower rates.
- Why is understanding tax brackets important for freelancers?
It helps you plan how much to save and reduces surprises during tax season.
- How often should freelancers check their tax bracket?
Check mid-year or anytime your income changes. Regular tracking supports better tax planning.
- Do business expenses affect your tax bracket?
Yes, expenses reduce your net income. Lower net income may place you in a lower bracket.
- Can seasonal income push freelancers into higher brackets?
Yes, peak-season spikes may move you upward. Planning ahead helps manage the additional tax.
- Should freelancers adjust estimated tax when income changes?
Yes, adjusting payments prevents penalties and large year-end bills.
- Do tax brackets influence retirement contributions?
Yes, retirement savings reduce taxable income and may keep you in a lower bracket.
- Can freelancers use apps to monitor income for bracket planning?
Yes, many apps track income, expenses, and estimated taxes to help you plan effectively.
- How do multiple clients affect tax brackets?
All client payments combined determine your taxable income, which may place you in a higher bracket.
- Do self-employment taxes affect your tax bracket?
No, your bracket is based only on taxable income. Self-employment tax is separate.
- Do tax brackets change each year?
Yes, the IRS may adjust them annually. Freelancers should check current rates before planning.
- Can freelancers legally lower their tax bracket?
Yes, deductions and retirement contributions can lower your net income.
- What happens if freelancers underestimate their bracket?
They may face penalties, unpaid tax, or a large bill at year-end.
- Can freelancers plan cash flow around their bracket?
Yes, understanding how much tax you’ll owe helps you save the right amount.
- Do tax brackets affect long-term financial planning?
Yes, they guide annual savings, income goals, and tax strategy decisions.








